项目信息
Project Info
| 团队规模 | 10+ |
| 角色 | TA 渲染算法 |
| 职责 | 高性能平滑圆角算法、抗锯齿及曲线形状定义; 高性能模糊及混色算法; 高性能弥散阴影算法。 |
| 持续时间 | ~ 2年 |
| 平台 | HyperOS 1.0/2.0 |
| 技术栈 | FigmaReactGLSLSKSL |
前言
Introduction
操作系统需要确保将注意力让给用户此刻关心的内容和任务,因此系统内的美学表达必须 克制收敛。 在这个基本原则下,基于原研哉先生提出的 “生命感” 美学理念上,我们将系统中最基础的元素抽离出来, 重新思考,辅以最先进的渲染技术,打造了系统高级材质 1.0。
The operating system needs to ensure that the user's attention is focused on the content and tasks that are important to them at the moment, so the aesthetic expression within the system must be restrained and convergent. Based on the aesthetic concept of "Alive" proposed by Mr. Kenya Hara, we have extracted the most basic elements from the system, rethought them, and created Advanced Material Design 1.0 with the most advanced rendering technology.

系统的元素需要适应不同尺寸/类型的设备、不同方式的交互、不同的光照环境、不同的动画效果、不同的内容展示等, 并表现良好,犹如生命体在不同环境中都具备的自适应能力。
The elements of the system need to adapt to different sizes/types of devices, different ways of interaction, different lighting environments, different animation effects, different content displays, etc., and perform well, just like the adaptive ability possessed by living organisms in different environments.
问题
Problem
- 如何让界面元素在任何场景下都能被清晰识别、不打扰。
- 如何塑造高级感,支撑集团高端化战略。
- 如何在最小的成本下,实现覆盖最广的视觉焕新。
- How to make the interface elements clearly identifiable and non-disturbing in any scene.
- How to create a sense of luxury to support the group's strategy.
- How to achieve the widest visual renewal coverage at the lowest cost.
范围
Scope

1. 圆角
1. Rounding Corner
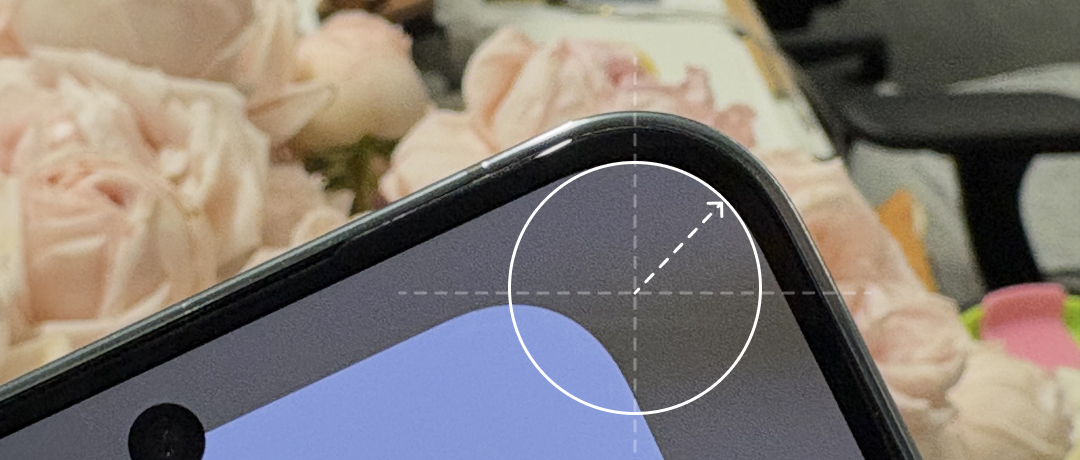

硬件边框在制造过程中需要考虑应力影响,因此会在手机四周倒角。随着全面屏的普及, 显示屏为了最大程度利用空间,也采用了圆角设计。为了保持一致性,软件也开始在窗口上使用圆角设计。
The hardware frame needs to consider the stress impact during the manufacturing process, so it will be chamfered around the phone. With the popularity of full-screen displays, the display screen also adopts a rounded corner design to maximize space utilization. To maintain consistency, software also began to use rounded corner design on windows.
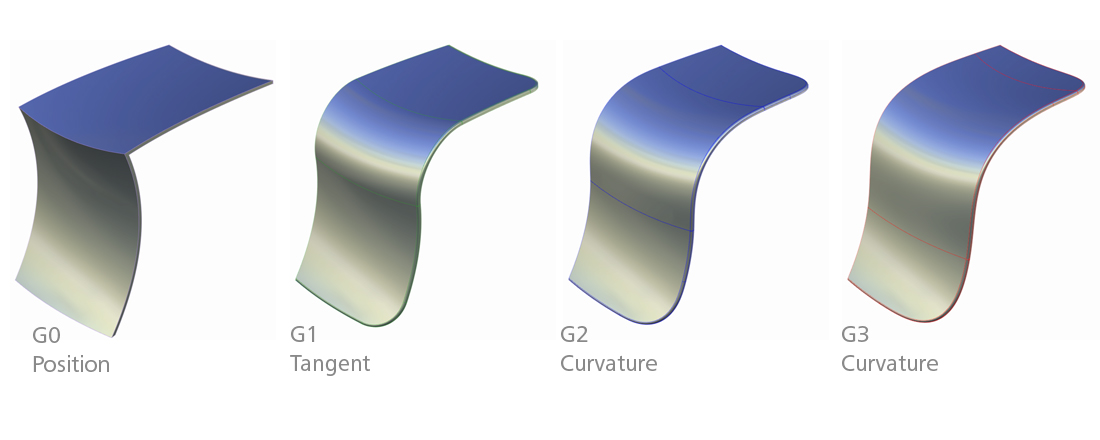
究其根源,圆角的设计是为了提高生产良品率,提升设备使用寿命,在光照下提供柔和的全反射。 分析并提升圆角曲线的 曲率连续性 是达到这一切的必要手段。
At its root, the design of rounded corners is to improve the yield of products, extend the service life of devices, and provide soft total reflection under illumination. Analyzing and improving the curvature continuity of the rounded corner curve is a necessary means to achieve all of this.
1.1. 曲率连续性
1.1. Curvature Continuity
曲面曲率在工业设计中被广泛应用,通过提升曲率连续性,可以减少光线反射,减少材料应力,提升视觉舒适度。对于不同的曲率要求,
数学上也有十分趁手的工具,例如 Nurbs, Bezier, B-Spline 等。
Surface curvature is widely used in the automotive industry design. By improving the curvature continuity, light reflection can be reduced, and visual comfort can be improved.
For different curvature requirements, there are also very handy mathematical tools, such as Nurbs, Bezier, B-Spline, etc.
对任何一条参数曲线,,可以通过以下公式对各点处的曲率进行计算。
For any parametric curve, , the curvature at each point can be calculated by the following formula.
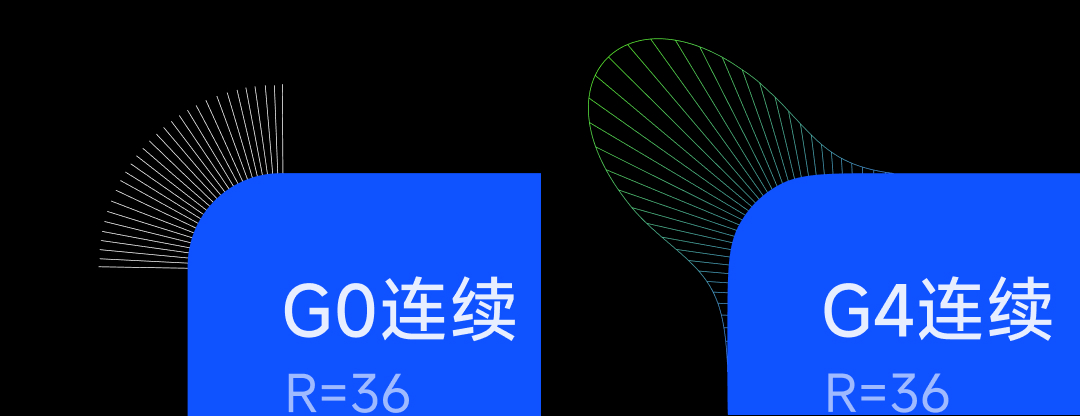
1.2. 正圆圆角与G4连续平滑圆角
1.2. Circular Rounded Corner and G4 Continuous Smooth Rounded Corner
我们最常用的正圆圆角 (左) 在与直线相交时,曲率突变,加上屏幕像素的限制,会导致视觉上的不连续感。 而我们提出的高级材质圆角 (右) 通过曲率连续性的提升,使得曲线在与直线相交时,曲率平滑过渡,视觉上更加舒适。
The most commonly used circular rounded corners (left) have a curvature mutation when intersecting with a straight line. In addition to the limitation of screen pixels, it will cause a visual discontinuity. The advanced material rounded corners (right) we propose smooth the curvature transition when the curve intersects with a straight line by improving the curvature continuity, making it more visually comfortable.
除此之外,不同屏幕的像素密度、亚像素排列方式、亮度等因素都会影响平滑圆角抗锯齿,从而影响视觉效果。 我们使用放大设备单独对不同设备、不同显示区域、不同显示分辨率的圆角进行了矫正,以保证视觉效果的一致性。
In addition, factors such as the pixel density, sub-pixel arrangement, brightness of different screens will affect the anti-aliasing of smooth rounded corners, thereby affecting the visual effect. We use a magnification device to correct the rounded corners of different devices, different display areas, and different display resolutions separately to ensure the consistency of the visual effect.
![]()
在实际应用中,屏幕上会同时存在数十个甚至上百个圆角,如何在保证性能的前提下,实现曲率连续性的提升,是我们需要解决的问题。
In practical applications, there will be dozens or even hundreds of rounded corners on the screen at the same time. How to improve the curvature continuity while ensuring performance is the problem we need to solve.
在这里我们使用了一系列实时渲染技术,通过利用 GPU 并行计算能力,整合安卓渲染流程,最终在全平台上实现了高性能的平滑圆角算法。 具体的平滑圆角算法和曲线生成方式因为 NDA 限制,无法在此展示。
Here we use a series of real-time rendering technologies, integrate the Android rendering process by utilizing the parallel computing capabilities of the GPU, and finally achieve a high-performance smooth rounded corner algorithm on all platforms. Due to NDA restrictions, the specific smooth rounded corner algorithm and curve generation method cannot be displayed here.
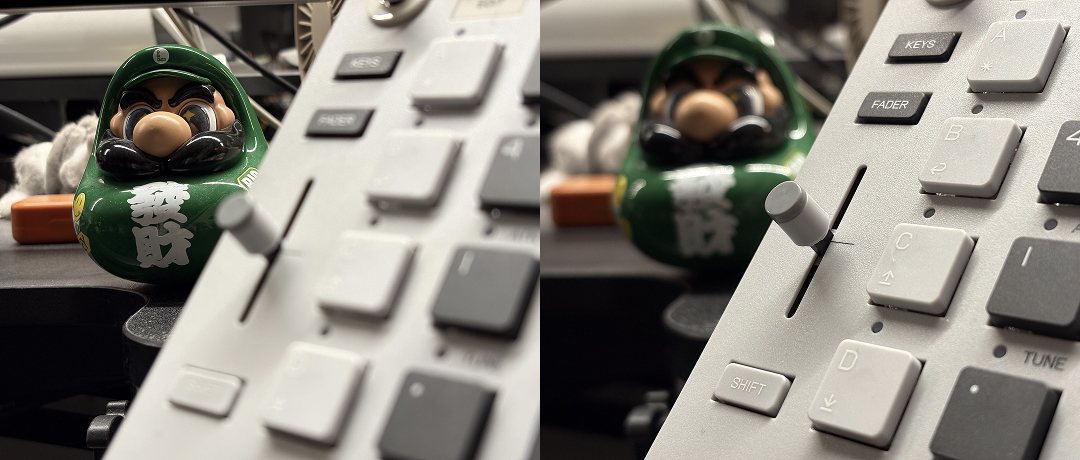
1.3. 前后对比
1.3. Before and After

我们不仅仅一味追求圆角的平滑度,而是尽可能保证在系统内的任何使用场景中都能与其他元素配合达到整体视觉协调。 一圆角矩阵排列时所呈现的负形空间为例。 如果只是单纯地追求圆角平滑度,拥有完美解析式的超椭圆将会是更好的选择,因为它很显然满足无穷阶曲率连续。
We do not just seek the smoothness of rounded corners, but strive to ensure that in any use scenario, they can harmonize with other elements to achieve a unified visual effect. A negative space example is when rounded corners are arranged in a matrix. A perfect ellipse which satisfies infinite curvature continuity can be a better choice if we only seek the smoothness of rounded corners.

但是当我们观察超椭圆所组成的负形空间时很容易发现,由于超椭圆圆角的凸起更明显,直线部分的长度无限趋近于零, 导致超椭圆所组成的负形空间非常复杂,在与其他直边元素配合时无法达到整体视觉协调。
But when we observe the negative space composed by the hyper-ellipse, it is easy to notice that the convexity of the hyper-ellipse corners is more obvious, and the length of the straight line part approaches infinity, resulting in a very complex negative space that cannot be harmonized with other straight-edge elements.
不仅仅是视觉上,超椭圆直线部分的长度无限趋近于零,这意味着在性能优化阶段将无法通过切割九宫格排除非必要渲染元素。 这将导致在标准圆角下,功耗相比于我们的平滑圆角高出 。 仅仅是圆角曲线的选择就可以对最终性能产生如此巨大的影响,这是只有改进生产流程才能带来的收益。
Not only visually, but the length of the straight sections of a superellipse approaches zero infinitely, which means that during the performance optimization phase, it will be impossible to exclude unnecessary rendering elements by slicing the nine-grid. This will result in power consumption being higher under standard rounded corners compared to our smooth rounded corners. The choice of corner curvature alone can have such a significant impact on final performance, which is a benefit that can only be achieved by improving the production process.

经过三个团队一年多的努力,平滑圆角正式进入 Hyper OS 1.0 系统固件。向4亿小米个人终端用户分发。
Through a year of effort by three teams, the smooth rounded corners have finally entered the Hyper OS 1.0 system firmware. We have distributed it to 4 million personal devices of Xiaomi.
2. 模糊
2. Blur
2.1. 任务、注意力和舞台
2.1. Window, Attention and Stage
操作系统一个非常重要的部分是协助用户更好地管理多任务场景。现实世界的任务是复杂的、非线性的。 用户的注意力正如硬件设备的储存和计算资源一样,是需要精心调度的。
A very important part of the operating system is to help users better manage multitasking scenarios. Real-world tasks are complex and nonlinear. User attention, like the storage and computing resources of hardware devices, needs to be carefully scheduled.
我们尽可能的将复杂任务拆解成线性步骤以保护用户的注意力,但在多个任务纠缠的时候, 用户不可避免的需要在多个上下文之间切换。如何帮助用户更快地调度注意力,是操作系统需要解决的问题。
We try to break down complex tasks into linear steps as much as possible to protect the user's attention, but when multiple tasks are entangled, users inevitably need to switch between multiple contexts. How to help users schedule attention more quickly is a problem that the operating system needs to solve.

在这里,我们提出了 舞台 的概念。舞台中心是用户当前关注的任务的视觉表现区域,是用户当前注意力的焦点。 而舞台其他区域则是余光的范围,他们需要适时地退让,以保证用户的注意力不被分散。
Here, we propose the concept of Stage. The center of the stage is the visual performance area of the task that the user is currently focusing on, which is the focus of the user's current attention. The other areas of the stage are the range of peripheral vision, and they need to retreat in time to ensure that the user's attention is not distracted.
2.2. 高斯模糊
2.2. Gaussian Blur
我们可能需要谈论一点点数学,这只是为了明白我们工作的基线。
真实世界的模糊效果是由光学系统产生的,本质上是多个不同区域的光线被投射到成像平面的同一个像素上。 我们可以用高斯模糊在数值上近似模拟一个理想小孔成像。 高斯模糊是一种图像模糊滤波器,它用正态分布计算图像中每个像素的变换。在二维空间定义为:
其中 是模糊半径 (), σ是正态分布的标准偏差。在二维空间中,这个公式生成的曲面的等高线是从中心开始呈正态分布的同心圆。 类似高斯模糊的图像操作在数学上成为卷积。维基百科 上有非常清晰的解释,感兴趣的话可以进一步阅读。
高斯模糊最大的问题是性能开销。对于一个 1920x1080 的屏幕,4个色彩通道,模糊半径为 10 的高斯模糊的计算量是:
而我们大多数场景使用的是 60~100 的模糊半径,这个数字会翻 ~ 倍。
最基本的优化手段是对卷积核进行线性分解,通过横、竖两个 render pass 分别进行计算, 这样计算量可以降低到:
仅靠拆解两个 render pass 即可获得 5 ~ 10 倍性能收益,不考虑其他因素,我们至少拥有可以在移动设备上实时交互的可能。 但这还是远远不够,用户不可能接受一台手机只是因为几个动画每3个小时就得充一次电。
游戏行业还有另外一个手段用来降低运算开销:降低渲染分辨率。这个方法在高斯模糊这个场景里显得尤其可行,毕竟反正都要模糊, 降采样带来的瑕疵混在高斯模糊里几乎是不可察觉的。
具体的方案受限于 NDA 无法披露,在我们最终的测试中,对 1920x1080 进行 0 ~ 200 px 的高斯模糊, 可以将帧耗时控制在 个时钟周期。自此,HyperOS 结束了 iOS 长达 7 年的模糊垄断, 实现了全系统的高斯模糊效果。这是跨部门三个团队长达一年的艰苦付出取得的成果。
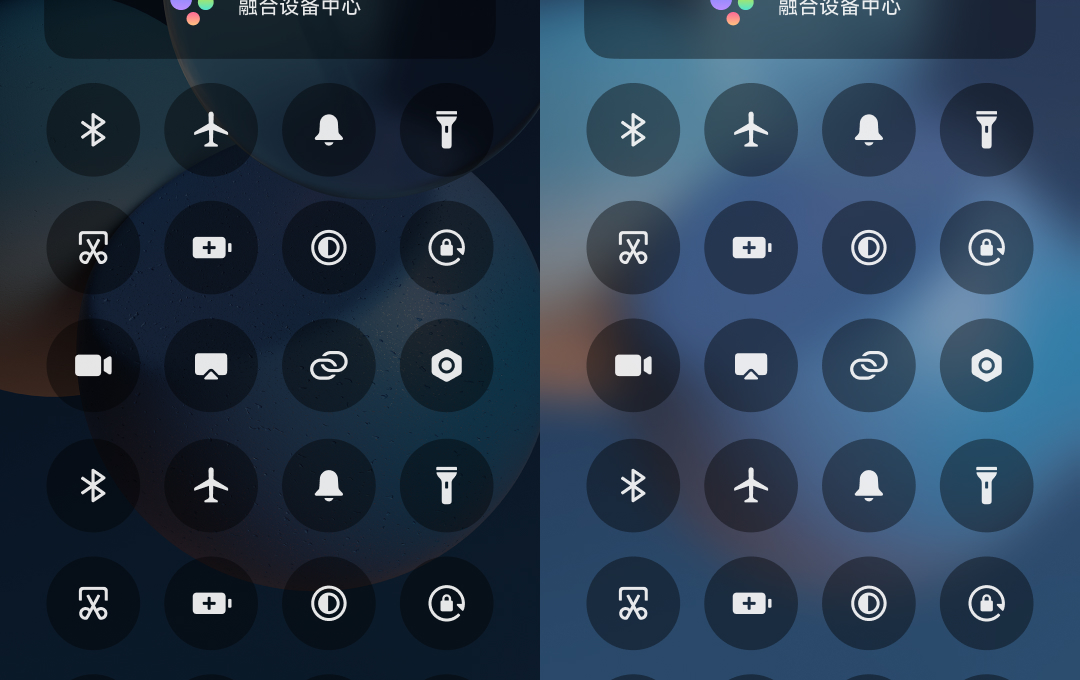
2.3. 前后对比
2.3. Before and After
2.4. 下一步 - 渐进模糊
2.4. The next step - Progressive Blur
实时渐进模糊带来的超现实观感开启了非常具有想象空间的视觉表现。
